Diabetes is a long-term medical condition. It affects many people globally. It has high blood sugar levels and can cause symptoms and complications. But does falling asleep after eating mean diabetes? This guide will explore the question and related concerns. We will explore other causes of falling asleep after eating and explain how to recognize signs of diabetes.
Is Falling Asleep After Eating a Sign of Diabetes?
The Basics of Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are high. There are two types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition. The immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 diabetes need insulin injections for blood sugar control.
Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 Diabetes is common. It is linked to a poor diet, a lack of exercise, and obesity. Type 2 diabetes makes the body resistant to insulin. The pancreas might not produce enough insulin to control blood sugar levels.

Postprandial Somnolence Explained
Postprandial somnolence is feeling sleepy after eating. It is also known as Food Coma! Many people experience this. It can happen for different reasons, like the meal and individual factors. Is it a sign of diabetes?
Let’s look at the connection between diabetes and postprandial somnolence.
Understanding Sugar and Diabetes
Sugar consumption and diabetes have a controversial and concerning relationship. Sugar doesn’t cause diabetes, but too much sugar can lead to Type 2 diabetes. This is how it works.
- Eating sugary foods or drinks makes your blood sugar go up.
- Your pancreas releases insulin to transport sugar into cells for energy.
- Eating too much sugar can cause insulin resistance, which is a sign of Type 2 diabetes.
- Insulin resistance makes it hard for your body to control blood sugar.
Does falling asleep after eating sugar mean you have diabetes? If you want to eat sweet, please visit our 27+ yellow fruits for further information.
The Sugar Crash Myth
Eating sugary foods can make you sleepy because of the “sugar crash.” The crash happens when your blood sugar spikes after eating sugar and then quickly drops, causing tiredness and sleepiness.
Sugar crashes are real. but they don’t mean diabetes. Anyone can have a sugar crash after eating or drinking a lot of sugar, even if they don’t have diabetes. Falling asleep after a sugar crash is due to changing blood sugar levels, not diabetes.

Post-Meal Fatigue: Diabetes Fatigue After Eating
Does feeling sleepy after eating mean you have diabetes? Many people feel sleepy after eating, and it’s usually not a health problem. Post-meal fatigue can happen for various reasons.
- Digestion: After eating, blood flow is directed to the digestive organs. This can make you feel tired because less blood is available for other activities.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: The parasympathetic nervous system becomes more active after a meal. It promotes relaxation and can make you feel sleepy.
Falling Asleep After Eating Sugar: CONCLUDED
Feeling sleepy after eating is not always a sign of diabetes. People without diabetes can feel tired after eating, especially if they eat a lot or have a meal high in carbohydrates. Consider other symptoms and factors when assessing diabetes.

How Do I Know if I Have Diabetes?
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of wounds.
Knowing the signs and symptoms of diabetes is important for early detection and treatment. Falling asleep after eating or feeling tired after a meal can be a symptom of diabetes. Other common indicators of diabetes include:
- People with diabetes urinate more often because their bodies get rid of extra glucose through urine.
- Increased urination can cause dehydration and make you feel very thirsty.
- Some people with undiagnosed diabetes lose weight without knowing why, even if they still feel hungry.
- High blood sugar levels can make your vision blurry.
- People with diabetes may experience slower healing of wounds and sores.
- Nerve damage from diabetes can cause tingling or numbness in the extremities.
- Diabetes weakens the immune system. This makes people more likely to get infections.
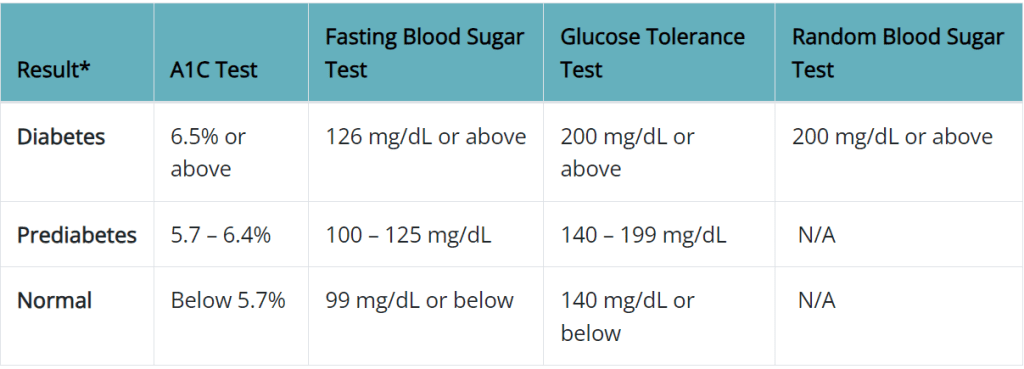
Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes
If you think you might have diabetes or have symptoms, see a doctor to get checked. Common diagnostic tests for diabetes include:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
The fasting blood sugar test measures your blood sugar level after not eating overnight. A blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or higher may mean diabetes.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) requires fasting overnight. After that, you drink a sugary solution. Blood sugar levels are tested regularly. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher two hours after drinking glucose may indicate diabetes.
Hemoglobin A1c Test
The hemoglobin A1c test measures your average blood sugar levels for the past two to three months. A level of 6.5% or higher means diabetes.
(SOURCE)
If you have diabetes, your healthcare provider will help you make a plan. This plan might include lifestyle changes, medications, and checking your blood sugar regularly.
Managing Post-Meal Sleepiness
If you have diabetes and feel very sleepy after eating, it’s important to work with your healthcare team to manage your condition well. Consider these strategies:
Balanced Meals
Eat balanced meals with carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. It helps stabilize blood sugar levels after eating.
Regular Monitoring
Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Identify patterns and make adjustments as needed.
Medication Management
Take your prescribed diabetes medication as directed to keep your blood sugar levels stable.
Timing of Meals
Pay attention to when you eat. Avoid big meals before bed.
Physical Activity
Exercise regularly to manage diabetes. Exercise helps control blood sugar levels.

Other Causes of Postprandial Somnolence (Falling Asleep After Eating)
Diabetes can make you sleepy after eating, but other things can too. Consider these factors before concluding that diabetes is the only cause of your symptoms.
Non-Diabetic Factors
Meal Size and Composition
Eating a big meal, especially one with lots of carbs, can make you feel sleepy afterwards. The body diverts energy to digestion, so this is a normal response.
Food Intolerances
Some people get tired after eating certain foods due to food intolerances or sensitivities. Dairy products and gluten-containing foods are often to blame.
Alcohol Consumption
Drinking alcohol with food can make you feel sleepy because it affects your nervous system.

Psychological and Environmental Influences
Stress
Stress can affect your digestion. It can cause discomfort after meals and make you feel sleepy.
Lack of Sleep
Not getting enough sleep can make you feel tired during the day. Eating can make this fatigue worse.
Environment
Temperature, lighting, and noise can affect how sleepy you feel after eating.
Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders like sleep apnea or narcolepsy can make you feel very sleepy during the day.
Sometimes, people might think that this sleepiness is because they ate too much. Falling asleep after eating can be a sign of diabetes, but not always. Diabetes has symptoms like fatigue. Feeling sleepy after a meal can have other causes.
If you feel sleepy after meals or worry about diabetes, talk to a doctor. They can do tests, check your health, and help you manage your symptoms or condition. Managing diabetes involves lifestyle changes, taking medication, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. You can improve your quality of life by working closely with your healthcare team.
FAQs
Is it normal to sometimes fall asleep after eating?
Feeling sleepy after eating a big or carb-heavy meal is normal. If it happens often or doesn’t go away, you should look into it more, especially if you have other diabetes risk factors.
Does postprandial somnolence always mean diabetes?
Postprandial somnolence and diabetes Post-meal sleepiness can be linked to diabetes, but it can also be caused by factors such as meal size, composition, stress, and sleep disorders.
How to avoid feeling tired after eating?
Avoid feeling tired after eating with these tips:
- Eat healthily.
- Control your food intake.
- Regularly check your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes.
- Stay hydrated.
- Regular exercise.
- Manage stress and get sufficient sleep.
When to see a doctor for post-meal sleepiness?
See a doctor if you feel sleepy after eating frequently. It’s crucial if you have other symptoms or risk factors for diabetes. A healthcare provider can test and check you to make a proper diagnosis.
Can medication treat diabetes-related fatigue?
Diabetes-related fatigue may require medication or insulin therapy. Your healthcare provider will treat you accordingly.











